ASHL Paper Reading Notes
Published:
ASHL: An Adaptive Multi-stage Distributed Deep Learning Training Scheme for Heterogeneous Environments
Overview
Heterogeneous Environments: clents have different computation and communication capabilities.
ASHL consists of three main schemes:
- a profiling scheme.
- a hybrid-mode training scheme (including a fast convergence AHL stage.
- a fine-tuned SHL stage), and a communication compression scheme.
Profiling scheme is used to probe the capabilities of the workers for task scheduling.
AHL stage is to make the model quickly converge.AHL adopts an asynchronous communication strategy and a lager tolerable training iteration variance between diiferent workers.
SHL is to improve model convergence. SHL uses a semi-asynchronous communication strategy and adopts a high communication frequency. SHL also adopts a smaller tolerable training iteration variance between different workers to carefully achieve the model conver- gence.
Background knowledge
Classic parameters models
- Bulk Synchronous Parallel(BSP)
- Asynchronous Parallel(ASP)
- Stale Synchronous Parallel(SSP)
- Local SGD
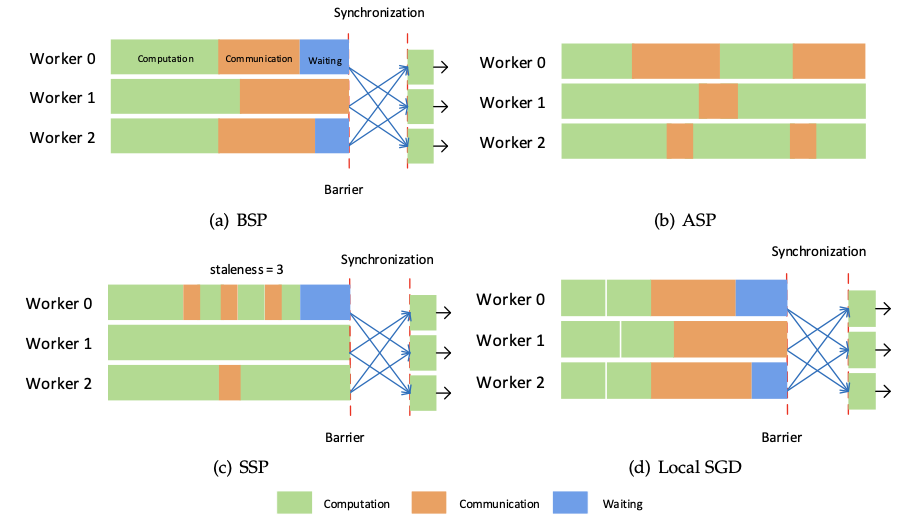
SSP sets an upper bound threshold for the iteration variances between workers. As long as the max iteration difference between workers is less than the given threshold, the workers are allowed to proceed to the next iteration. Otherwise, the fastest worker will stop and wait for the slowest worker.
Local SGD performs the synchronization process after all workers trained their data with the mini-batch SGD algorithm for H iterations locally.
Detail
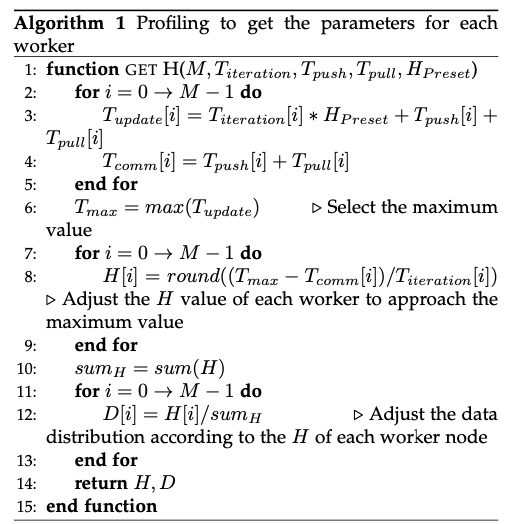
Profiling
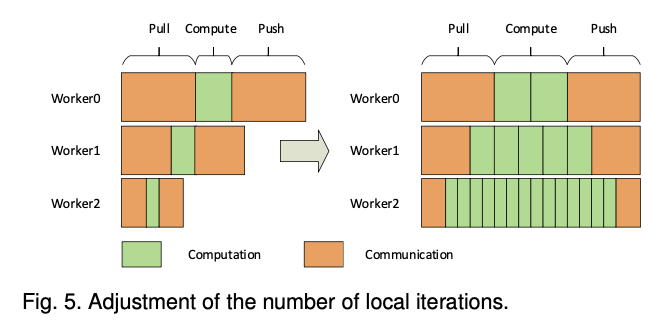
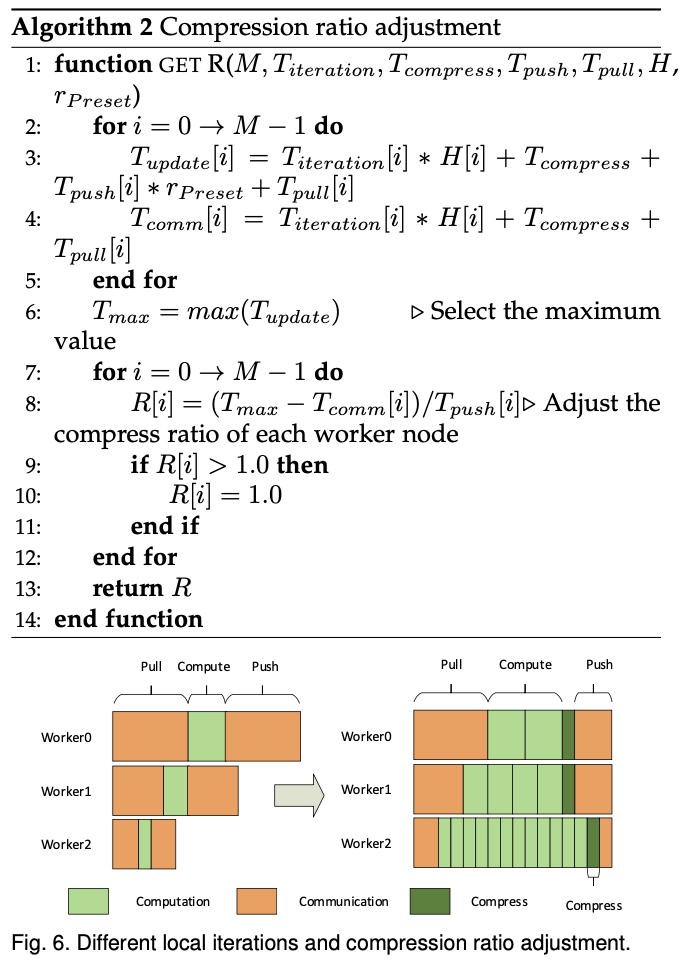
To eliminate the waiting time as much as possible, Author adjust the local iteration times of each worker node by adjusting the local iteration number. They make the local iteration time + communication time (includeing $T_{pull}$ and $T_{push}$) between the worker nodes as consistent as possible.
When the difference between H is large, the worker nodes with small H will undergo more parameter synchronizations to train all their data, while the worker nodes with large H can train all their data in less parameter synchronization time. They allocate data of different sizes to each worker node according to the difference of H for each worker node to improve the convergence.
Hybird-mode Training
Considering the fast convergence speed of the model in the early stage and the large changes in model parameters, this stage does not require too intensive communication, so using a larger number of local iterations H in the AHL stage can reduce communication and speed up the model convergence.
In the SHL stage, the model convergence is gradually approached in a fine-grained manner. So, we use an overall smaller H and more frequent communication in the second half to obtain a better convergence effect. To do this, we need to determine multiple sets of H values during the profiling process.
Commuication Compression
In each worker, the parameter differences ∆wi are compressed (the classic top-K method is used here) and then uploaded. On the PS side, first, decompress each received ∆wi, and then use them to update the global parameters.
we adjust the upload time Tpush by adjusting the compression ratio, we can further reduce the difference of a parameter update between each node by adjusting $T_{push}$